 |
| http://eduframe.net/andc |
NOTE:
A simple way to remember is when V2 is higher then that op amp will cause ground for the circuits (current flow from Vo to Vcc-) while when V1 is higher then op amp will provide a voltage output ( current flow from Vcc+ to Vo)
IDEAL OP AMP:
When talking about "ideal op amp" it means that its produces the max it can with little voltage and the minimalist current possible also when connected to a frequency machine when changed without effect the ideal possible operation of op amps also heat factors as some component generate heat more than other but a ideal op amp wouldn't be bother by any heat factor and operate to its max ideally.
Non inverting op amps would allow voltage flow threw op amp output for the circuit to continue to ground. To calculate Vout would be:
 |
| www.wikipedia.com |
Vout = Vin x (+1 (R1/R2)) If voltage was 12v, R1 AND 2 were 100Ohms then it would be Vout = 12 x (+1(100/100)) = 24 Vout
Inverting op amps which allows current flow to threw the inverting terminal (-) and flow out the non- inverting terminal for current will flow from Vout which will be positive and needing to be ground the op amp helps to achieve goal. When used in this application then this would be used for grounding circuits because of the negative feedback.With the 12v on the inverting terminal the Vout will be a negative number.
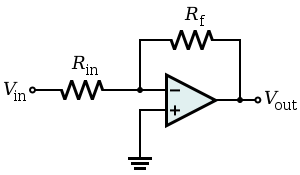 |
| www.wikipedia.com |
Vout = Vin x(Rin/Rf) 12Vin, Rin 100, Rf 100= Vout
Vout = 100/100 x 12= -12
This is one of many ways of using a op amp in application similar to relays, transistors etc, they take little amount of voltage/current and convert it into a more sufficient supply of voltage/current.







